How to compile and run C program using command line in Windows

This is one of the most frequently asked question to me. Creating and compiling a C program using an IDE is like waving some magic wand. However, a beginner must know how to compile and run C programs using command line in Windows based operating system.
To create a C program using command line you need two basic software’s.
- A text editor (such as Notepad or Notepad++ ).
- A C compiler.
You must have C compiler installed and configured on your computer before you proceed.
How to create a C program using Notepad (Windows)?
- Open notepad.
Hit windows button and type notepad in it.
Alternatively, hit Win + R , type notepad and hit enter to open notepad.
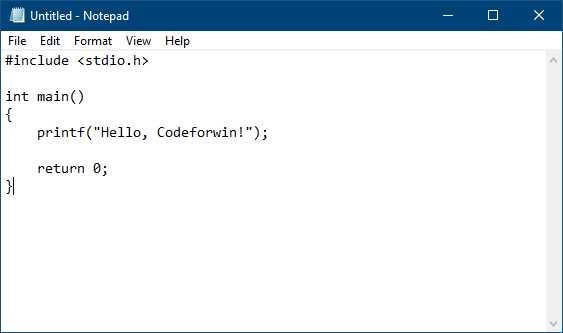
- Type C source code in notepad. For now do not care about what you are typing just copy paste the source code. We will have in depth discussion on C program structure later. Copy and paste the below source in your notepad.
#include int main()
Click on File → Save As in the menu bar. Alternatively, hit Ctrl + S to open Save As dialog box. 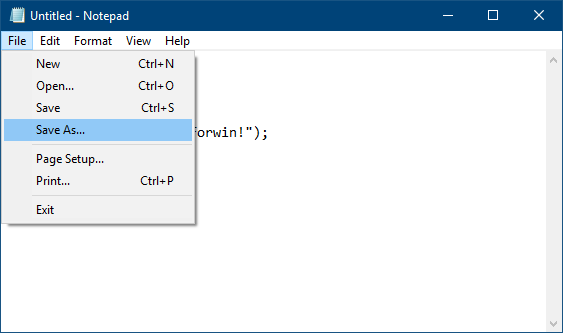 Give some name to your first C program. Add .c extension at the end of your file name. Also be sure not to save this file as plain text file. Change the plain text file option from Save as type option to All files.
Give some name to your first C program. Add .c extension at the end of your file name. Also be sure not to save this file as plain text file. Change the plain text file option from Save as type option to All files. 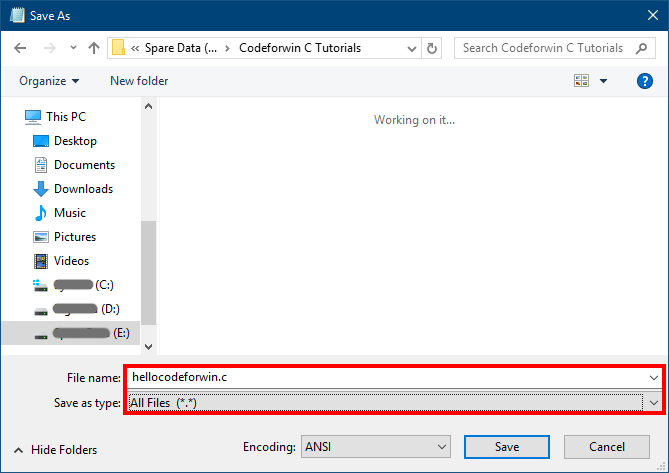
How to compile and run a C program using command line?
Once you created your first C program. It’s time for real action. A program is worthless until it is compiled and executed.
Syntax to compile single C program using GCC
gcc -o
Syntax to compile multiple files at once using GCC
gcc . -o
Syntax to run a C program
Example to compile and run above program
Before you compile and run the above C program. You must be in the same directory as of your C program. To test your program open command prompt and execute following commands.
gcc hellocodeforwin.c -o hellocodeforwin hellocodeforwin
C Programming
- C Fundamentals
- Introduction to C
- Set up C lab
- Create, compile and run
- Using Command line
- Using CodeBlocks
- Data types in C
- Variables and Expressions
- Defining Constants
- Typecasting
- Basic input and output
- Flow control statements
- Simple if
- If…else and if…else…if
- Nested if…else
- Switch case
- If…else…if vs switch…case
- for loop
- while loop
- do…while loop
- Nested loops
- break statement
- continue statement
- goto statement
- Infinite loops
- Functions in C
- Function arguments
- return statement
- Types of functions
- Recursion in C
- Variable length arguments (var-args)
- C local variables
- C static variables
- C global variables
- C storage classes
- C Arrays
- C multi-dimensional array
- C Arrays and functions
- C Pointers Introduction
- C Pointer arithmetic
- C Pointer to Pointer
- C Pointers and Array
- C const pointer and pointer to const
- C void pointer
- C Function pointer
- Compile time & runtime memory allocation
- Dynamic Memory Allocation
- C Structures
- C Unions
- C typedef





